SpringBoot
配置相关
配置注入实体类
编写实体类
1
2
3
4
5
6public class AppConfig {
String appId;
String apigwPublicKey;
String priKey;
String baseUrl;
}参数注入需要set方法,所以加上@Data注解
交由Spring管理当前对象,添加@Component注解
或在启动类添加@EnableConfigurationProperties({实体类class})
设置前缀,添加@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “app”)注解
在配置文件进行配置
1
2
3
4
5app:
appId: 123
apigwPublicKey: 456
priKey: 789
baseUrl: 0使用,在需要用到的类@Autowired AppConfig即可
配置提示
引入依赖
1 | <!--自定义配置处理器--> |
如果无效果,检查maven插件版本是否吻合,尝试install查看是否会报错
多配置切换
可同时定义多个配置文件,命名方式为“application-*.yml”,如
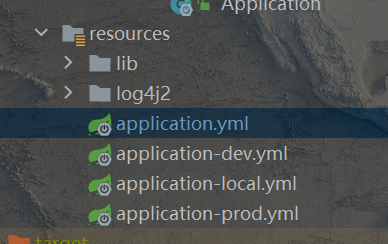
切换方法一:手动修改springboot配置文件
在application.yml中配置
1
2
3spring.profiles.active=dev
# spring.profiles.active=local
# spring.profiles.active=prod切换方法二:maven配置(maven变量注入)
maven在编译时可以动态决定当前编译环境
application.yml中配置为:
1
2# @@中变量名可自定义,但要与下面的配置中标签相同
spring.profiles.active=@profiles.active@maven中配置profiles内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30<profiles>
<!-- 本地 -->
<profile>
<id>local</id>
<properties>
<!--profile.active对应application.yml中的@profile.active@-->
<profile.active>local</profile.active>
</properties>
<activation>
<!-- 默认选择的配置 -->
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
<!-- 测试 -->
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<properties>
<!--profile.active对应application.yml中的@profile.active@-->
<profile.active>dev</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
<!-- 正式 -->
<profile>
<id>prod</id>
<properties>
<!--profile.active对应application.yml中的@profile.active@-->
<profile.active>prod</profile.active>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>该配置会在maven工具中生成profile菜单,可进行勾选
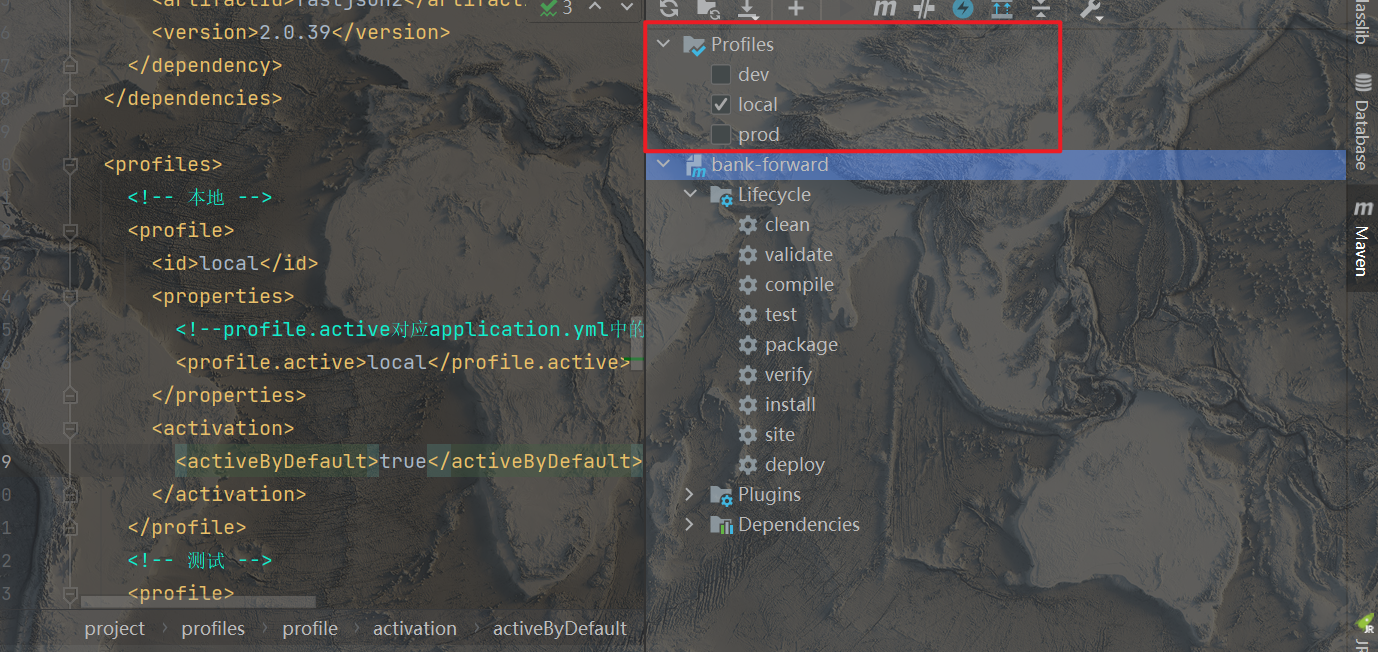
如果想要在编译时排除其他环境的配置,可以在pom中配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25<build>
<resources>
<!--排除配置文件-->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<!--先排除所有的配置文件-->
<excludes>
<!--使用通配符,当然可以定义多个exclude标签进行排除-->
<exclude>application*.yml</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
<!--根据激活条件引入打包所需的配置和文件-->
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<!--引入所需环境的配置文件-->
<filtering>true</filtering>
<includes>
<include>application.yml</include>
<!--根据maven选择环境导入配置文件-->
<include>application-${profile.active}.yml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
配置文件优先级
覆盖
对于key不同,则直接生效;
对于key相同的同名配置项,后加载会覆盖掉前加载,故而最终为后加载的配置项生效
本地配置
- 同文件名配置 *.yaml 加载先于 *.properties
- bootstrap配置 加载先于 application配置
- 不带profile的配置 加载先于 带profile的配置
故
- bootstrap.yaml
- bootstrap.properties
- bootstrap-{profile}.yaml
- bootstrap-{profile}.properties
- application.yaml
- application.properties
- application-{profile}.yaml
- application-{profile}.properties
nacos配置
- 本地配置 加载先于 nacos配置中心
- nacos配置中心上共享配置(见下说明) 加载先于 nacos配置中心该服务配置(见下说明)
- 不带profile的配置 加载先于 带profile的配置
- nacos配置中心因需要通过data ID指定(或者通过spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension指定后缀),所以对于Nacos配置中心上的某个Data ID而言,不会存在既加载其*.yaml又加载其*.properties的情形。
故
- 本地配置
- nacos配置中心共享配置(通过spring.cloud.nacos.config.shared-configs指定)
- Nacos配置中心该服务配置(通过spring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix和spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension指定)
- Nacos配置中心该服务-{profile}配置(通过spring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix和spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension、以及spring.profiles.active指定)
controller 请求参数注入命名转换
参考资料 springboot项目配置参数请求及返回均为下划线方式_springboot responsebody 指定返回的格式 为下划线分割_偶系渣渣灰的博客-CSDN博客
在配置文件中添加配置
1 | spring: |
CamelCase策略,Java对象属性:personId,序列化后属性:persionId
PascalCase策略,Java对象属性:personId,序列化后属性:PersonId
SnakeCase策略,Java对象属性:personId,序列化后属性:person_id
KebabCase策略,Java对象属性:personId,序列化后属性:person-id
SpringBoot与Spring的关系
Spring Boot 为Spring的扩展封装,免去了很多配置,使得使用spring更加便捷
SpringAOP
AOP 要达到的效果是,保证开发者不修改源代码的前提下,去为系统中的业务组件添加某种通用功能。比如添加日志等。AOP 的本质是由 AOP 框架修改业务组件的多个方法的源代码,AOP是代理模式的典型应用。
SpringIOC
Spring来控制对象的生命周期
DI:依赖注入,spring依赖注入,不用关心具体的实现,比如日志有多个框架,我们只需要知道spring会给我们提供,不需要了解底层用的哪个框架
SpringBoot自动装配原理
- @SpringBootApplication注解中引入了@EnableAutoConfiguration注解
- @EnableAutoConfiguration注解中引入了@Import注解
- @Import注解引入了一个deferredImportSelector对象,其功能为在springboot启动完成之后再引入,方便覆盖时判断如conditionOnBean
- 找到META-INF/spring.factories配置文件
- 过滤出所有的AutoConfiguration类
- 通过@Condition排除无效自动配置类
这些自动配置类都是以AutoConfiguration结尾来命名的,它实际上就是一个JavaConfig形式的Spring容器配置类,通过@Bean导入到Spring容器中,以Properties结尾命名的类是和配置文件进行绑定的。它能通过这些以Properties结尾命名的类中取得在全局配置文件中配置的属性,我们可以通过修改配置文件对应的属性来修改自动配置的默认值,来完成自定义配置
SpringBoot版本
- 版本号
Spring Boot 的版本号由 3 位组成,这里还是以上边两个版本为例,如下图:
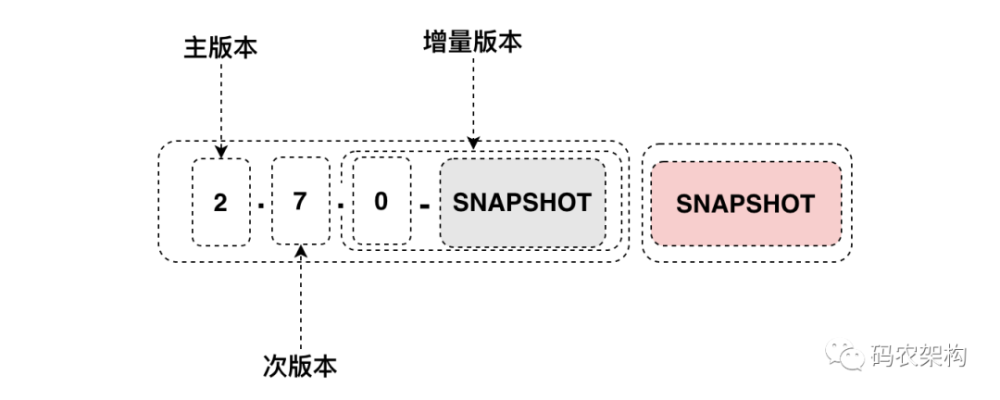
主版本:有可能进行大的架构调整,各大版本之间并不一定兼容
次版本:在主版本架构不变的前提下,增加了一些新的特性或变化
增量版本:bug 修复,细节的完善,用来描增量版本的,不一定是数字,例如:3.0.0-SNAPSHOT
发布状态
发布状态也有很多同行人称为发布计划,常见的有以下几个:
GA:General Availability,正式发布的版本,官方推荐使用该版本,国外很多项目都是使用GA来表示正式发布版本的
PRE:预览版,主要是用来内部开发人员和测试人员测试使用,因此不建议使用
SNAPSHOT:快照版,可以稳定使用,且该版本会一直进行小量的优化和改进
RC:Release,该版本已经相当成熟了,基本上不存在导致错误的BUG,与即将发行的正式版相差无几。
RestFul接口规范
RESTful的特点: a. 每个互联网资源都有一个唯一的URI地址; b. 通过操作资源的表现形式来操作资源; c. 一般情况下使用JSON格式来表示具体的数据; c. 使用HTTP协议进行客户端与服务端之间的交互,从客户端到服务端的每个请求都必须包含理解请求所必需的信息; d. 客户端使用GET、POST、PUT(patch)、DELETE 4个表示操作方式的动词对服务端资源进行“状态”操作。
- 命名必须全部
小写 - 资源(resource)的命名必须是
名词,并且必须是复数形式 - 如果要使用连字符,建议使用‘ - ’而不是‘ _ ’,‘ _ ’字符可能会在某些浏览器或屏幕中被部分遮挡或完全隐藏
- 易读
常用注解
启动注解
- @SpringBootApplication
- 启动类注解
- 包含@SpringBootConfiguration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan
- @SpringBootConfiguration
- 继承@Configuration,标注当前类为配置类,会将当前类中声明的一个或多个以@Bean注解标记的方法纳入spring容器中,且实例名就是方法名
- @EnableAutoConfiguration
- 将当前所有符合条件的配置都加载到当前SpringBoot创建并使用IOC容器。
- @ComponentScan
- 自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件或bean定义,最终将改些bean加载到容器中
- 可以通过basePackages等属性指定@ComponentScan自动扫描的范围,如果不指定,则默认Spring框架实现从声明@ComponentScan所在类的package进行扫描,默认情况下是不指定的,所以SpringBoot的启动类最好放在root package下。
Controller相关注解
- @Controller
- 控制器,处理HTTP请求
- @RestController
- 将方法返回的对象直接在浏览器上展示成json格式
- @RequestBody
- 通过HttpMessageConverter读取Request Body并反序列化为Object(泛指)对象
- @RequestMapping
- 会将 HTTP 请求映射到 MVC 和 REST 控制器的处理方法上
- @GetMapping / @PostMapping
- 将HTTP get / post请求映射到特定处理
取请求参数值
- PathVariable
1 | @Controller |
- RequestParam
1 | @RequestMapping("/getUser") |
- @RequestHeader 把Request请求header部分的值绑定到方法的参数上
- @CookieValue 把Request header中关于cookie的值绑定到方法的参数上
SpringBoot 核心功能
- 独立运行spring项目,springboot 可以以jar包的形式独立运行
1 | java -jar xx.jar |
使用嵌入式的Servlet容器,应用无需打成war包
大量自动配置,简化开发,可修改默认配置
提供starter简化Maven配置。Springboot提供了一系列的start pom用来简化maven依赖。如:常用的spring-boot-starter-web、spring-boot-starter-tomcat、spring-boot-starter-actuator
准生产环境的运行时应用监控
自动配置spring,Springboot会根据我们项目中类路径的jar包,为jar包的类进行自动装配bean。
应用监控。springboot提供了基于HTTP、ssh、telnet对运行时的项目进行监控。springboot提供了actuator组 件,只需要在配置中加入spring-boot-starter-actuator依赖,通过继承AbstractHealthIndicator这个抽象类, 然后在doHealthCheck()方法中检测服务健康的方法,就可以实现一个简单的监控。
idea构建spring boot 项目
- 脚手架使用阿里的,速度会快一点
- 记得配置maven的镜像,不然下载很慢
- 如无配置,可新建一个settings.xml
pom文件
管理依赖
启动类
一个普通的Java程序需要有一个入口,一般是某个类中的main方法。我们启动程序,就是运行这个 main方法。SpringBoot的主程序也就是整个项目的入口,同样会有一个main方法。SpringBoot项目就是从主程 序开始运行的。下图是一个实际项目中的主程序,对于SpringBoot程序来说,必须要用@SpringBootApplication 来标识启动类。其他的注解都是实际项目中为了实现其他的功能而添加的。
配置文件
application.properties
application.yml
配置文件的作用
修改SpringBoot自动配置的默认值 SpringBoot的底层把我们的常用配置都给我们配置好了,一般来说我们不需要去调整大部分的配置,直接使 用默认的配置就好。这也是SpringBoot“习惯大于配置”的思想。但有的时候默认值不符合我们项目的要求, 这个时候我们就可以通过配置文件来修改这些默认值
为程序添加变量
有的时候我们不会把所有的变量都写死在代码中,有些东西是会经常发生变化,或者不同环境的值不同。比如 对接系统接口的地址、数据库的连接信息等等。这个时候我们就可以将这些内容写在配置文件中,程序在使用 的时候,可以去读取配置文件中的值。
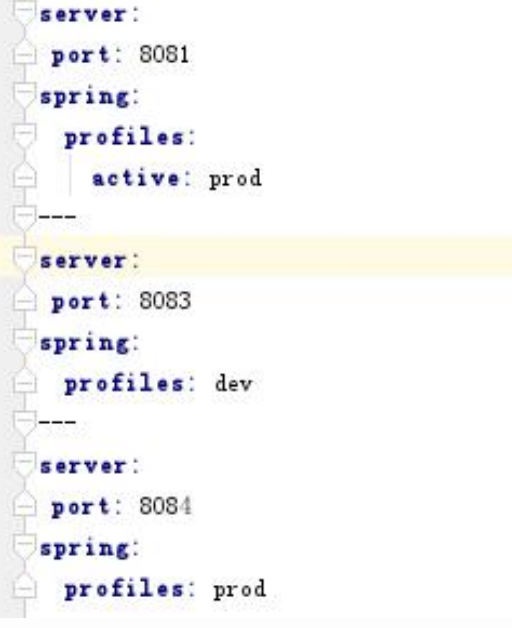
profile
Profile是Spring对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活、指定参数等方式快速切换环境 多profile文件形式: – 格式:application-{profile}.properties/yml: • application-dev.properties、application-prod.properties
入门案例
搭建一个spring boot 工程并开发几个简单的接口
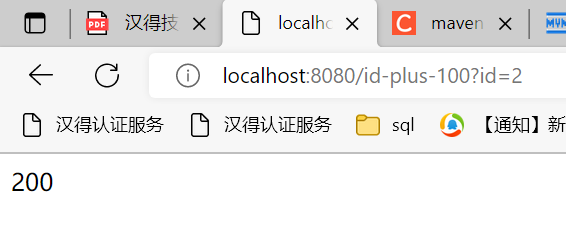
a. GET: 接口传入id参数,后端返回id*100后的结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11/**
* GET: 接口传入id参数,后端返回id*100后的结果
* @param id
* @return
*/
public String getIdPlus100(
Integer id
){
return String.valueOf(id*100);
}
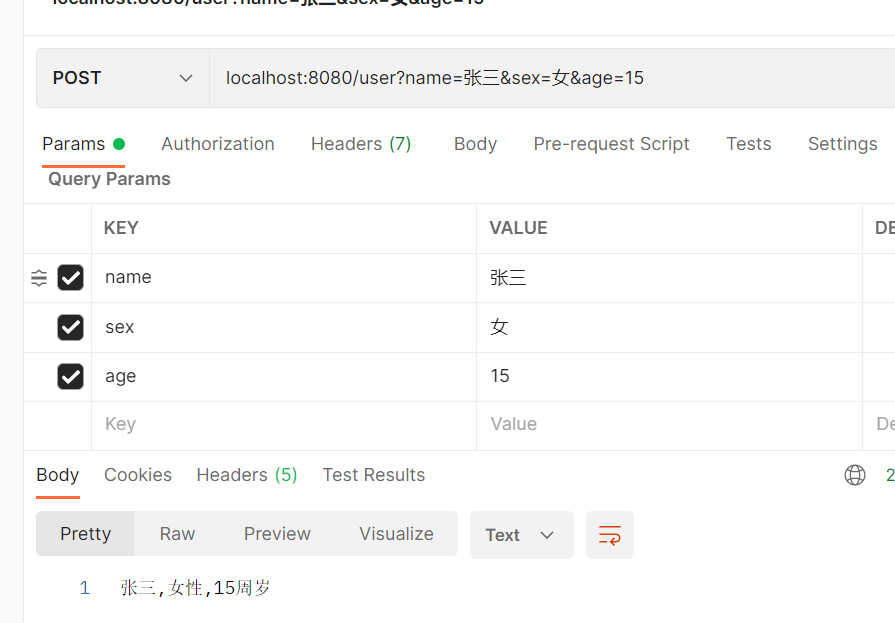
b. POST:接口传入{name: ”张三” ,sex: “男” ,age: “18”},后端返回“张三,男性,18周岁”
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15/**
* POST:接口传入{name: ”张三” ,sex: “男” ,age: “18”},后端返回“张三,男性,18周岁”
* @param name
* @param sex
* @param age
* @return
*/
public String postUser(
String name,
String sex,
Integer age
){
return String.valueOf(name+","+sex+"性"+","+age+"周岁");
}
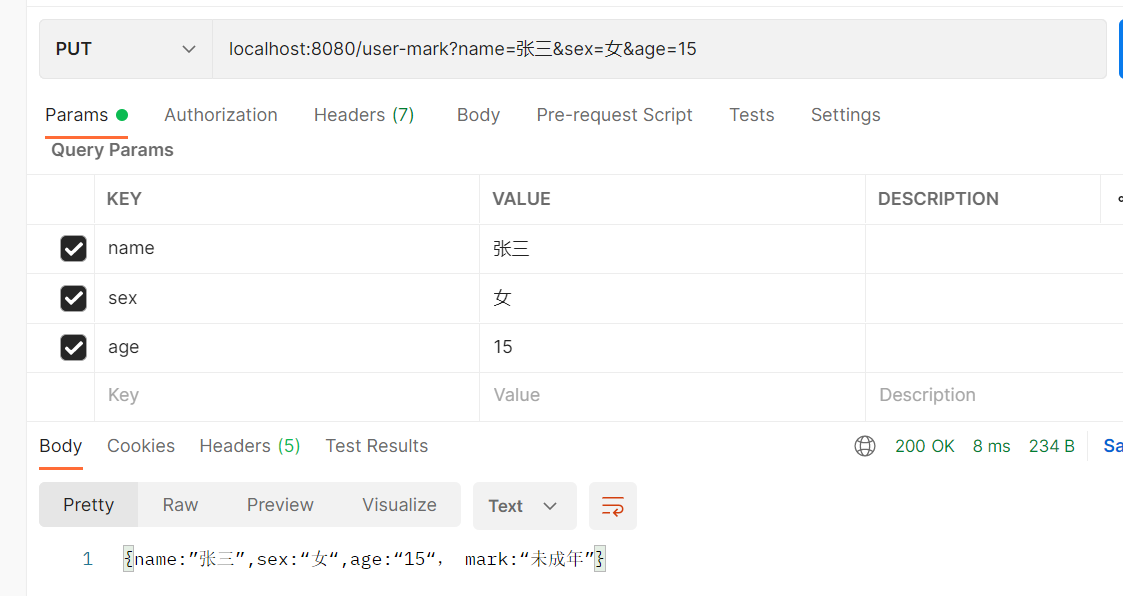
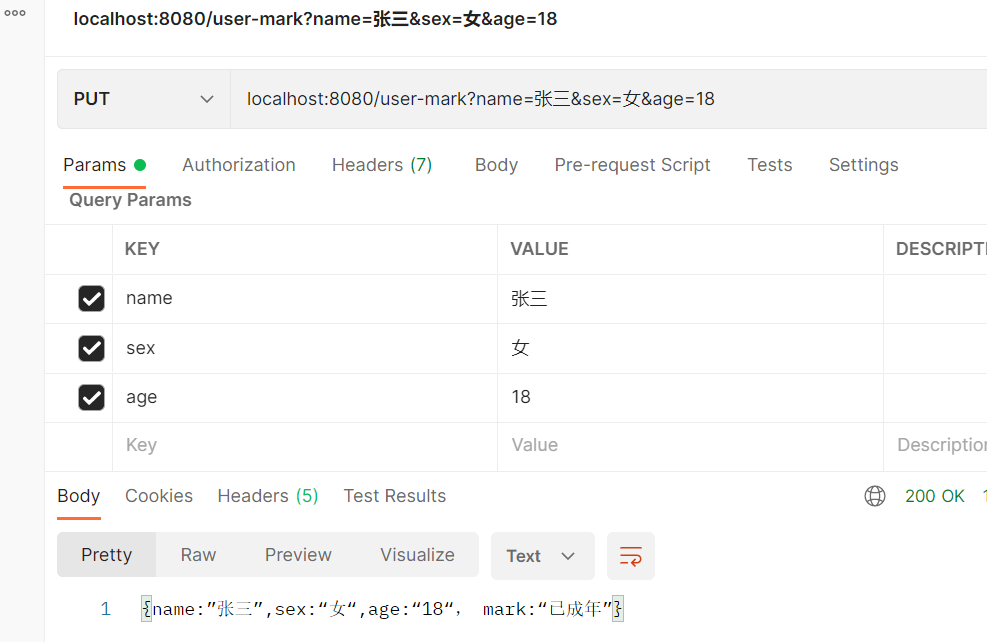
c. PUT:接口传入{name: ”张三” ,sex: “男” ,age: “18”} ,后端返回{name: ”张三” ,sex: “男” ,age: “18” , mark: “已成年”}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31/**
* PUT:接口传入{name:”张三”,sex:“男”,age:“18”} ,后端返回{name:”张三”,sex:“男”,age:“18”, mark:“已成年”}
* @param name
* @param sex
* @param age
* @return
*/
public String putUserMark(
String name,
String sex,
Integer age
){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("{");
sb.append("name:”");
sb.append(name);
sb.append("”,sex:“");
sb.append(sex);
sb.append("“,age:“");
sb.append(age);
sb.append("“, mark:“");
if(age >= 18){
sb.append("已成年”}");
}else {
sb.append("未成年”}");
}
return String.valueOf(sb);
}
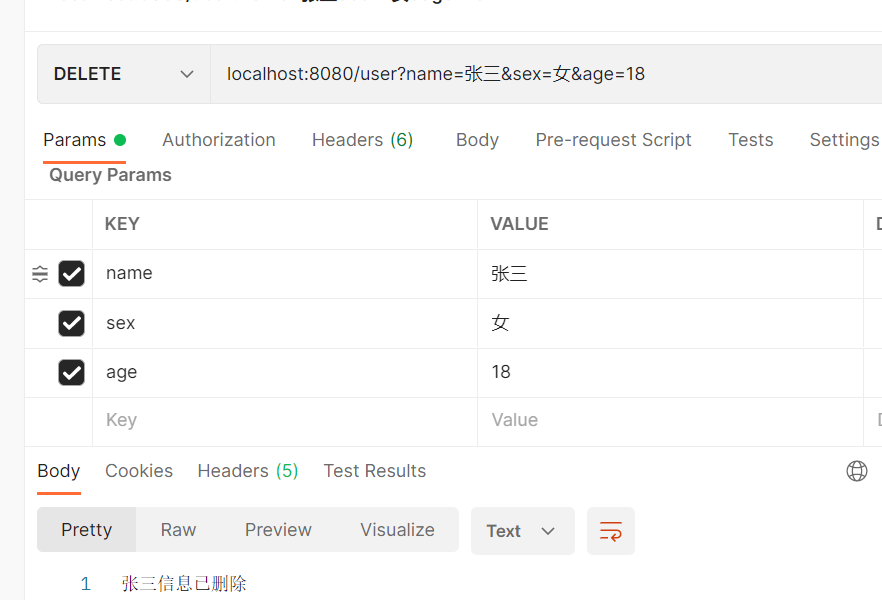
d. DELETE: 接口传入{name: ”张三” ,sex: “男” ,age: “18”} ,后端返回, “张三信息已删除“
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15/**
* DELETE: 接口传入{name: ”张三” ,sex: “男” ,age: “18”} ,后端返回, “张三信息已删除“
* @param name
* @param sex
* @param age
* @return
*/
public String deleteUser(
String name,
String sex,
Integer age
){
return String.valueOf(name+"信息已删除");
}
一个案例
引入依赖
1 | <dependency> |
Student表的增删改查
1 | package com.example.firstdemo.api.controller; |
1 |
|
ajax
1 |
|
1 | $(document).ready(function () { |
1 |
|
restful风格的前端请求
spring boot 默认关闭了隐藏方法过滤器,使得前端 form 无法发送 put 或者 delete 请求,需要在 yml 中开启 * spring: * mvc: * hiddenmethod: * filter: * enabled: true1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
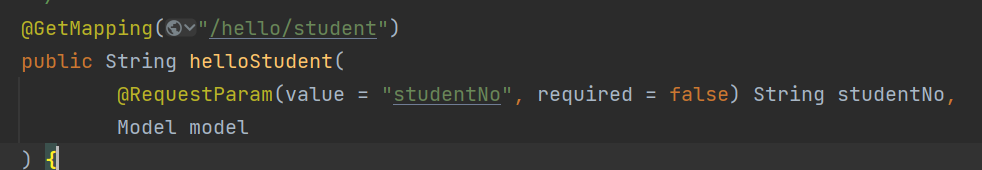
# required=false
某些请求参数不一定会传入,为了防止400错误,可使用 required = false来设置该参数
# thymeleaf非空判断
thymeleaf中如果要从一个对象中获取属性,但对象有可能为null,可使用问号进行非空判断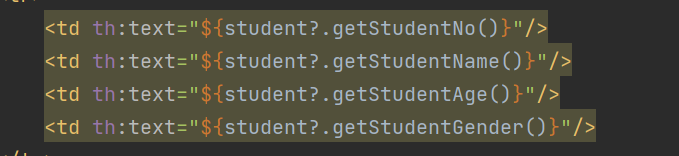
# ajax
- ```js
$.ajax({
type: "POST", // 发送的请求类型
contentType: "application/json", // 发送给服务器的编码类型
url: "/hello/student/core", // 请求地址
data: JSON.stringify(coreObj), // 发送的数据,这里使用JSON.stringify将一个对象转为JSON格式
dataType: 'json',//服务器返回的数据类型
cache: false,
timeout: 600000, // 超时毫秒
success: function (data) { // 请求成功后调用的函数
alert("插入成功");
// $("#core").prop("value",data.core)
},
error: function (){ // 请求失败调用的函数
alert("插入失败");
}
})
MultipartFile设置文件的大小
1 | //spring boot进行了集成,需要进行文件大小的设置 |
邮件发送
使用spring-boot-starter-mail
1 | mail: |
SpringBoot直接运行原理
打包的时候执行插件:spring-boot-maven-plugin
打包后会生成一个Far Jar,其中包含了应用依赖的jar包和SpringBootLoader相关的类
java -jar时查看jar包中的manifest.mf文件,其中指定了java运行主类MainClass与Spring运行主类StartClass
jar包中指定的主类是JarLauncher,其会创建一个ClassLoader来动态加载jar包中boot-lib下的jar包,并新开一个线程执行指定的StarClass中的main函数
这里其实想到了shade插件,shade插件的原理是将依赖的jar包解包之后直接包入成品jar包中,而不像springboot动态的去加载jar包。
SpringBoot连接数配置
1 | server: |
默认值可以在这里看
Q&A
并发量指的是连接数还是线程数
连接数最大的200个线程如何处理10000条连接
Tomcat的两种处理连接的模式,一种是BIO,一个线程只处理一个Socket连接,另一种是NIO,一个线程处理多个Socket连接,由于HTTP请求不会太耗时且多个连接一般不会同时来消息,所以一个线程处理多个连接没有太大问题多开线程与增加连接数
增加线程一个影响就是会增加线程切换时的上下文的切换时间,且线程增多,在核数不变的请宽心,每个线程分配到的时间片会变小,所以多开线程并不一定会提高处理效率
如果增加连接数,支持的并发量会提高,但是如果硬件条件没有提升,则并发量的提升只能是以牺牲响应时间为代价
SpringBoot启动速度优化
设置Bean为懒加载
启动是快了,但是初次执行慢了1
2
3spring:
main:
lazy-initialization: truespring5支持的创建扫描索引
引入需要的依赖,启动类上添加@Indexed注解,在打包时会创建扫描索引spring.components到META-INF文件夹中,索引中保存Bean的全类名,执行时直接从索引中读取,不再需要挨个查看类注解使用JDK17,其中提供了更优秀的垃圾回收器
使用SpringBoot3,其中提供了一个本地化的解决,执行更快
SpringBoot解决跨域
jsonp+callback
只支持get请求,前后端需要共同编码CORS(接口粒度)
CrossOrigin(源)注解标注在Mapping方法上WebMvcConfigurer(批量)
重写该接口的addCorsMappings方法,添加跨域配置CorsFilter(全局)
在容器中添加一个CorsFilter的Bean,需要浏览器支持NGINX(推荐)
在前端使用NGINX部署的情况下,将访问后端的请求改为访问前端服务器,但通过路径(比如添加一个前缀)区分,接着在NGINX中添加配置进行代理转发。因为NGINX是不会有跨域限制的,且浏览器发现你访问的还是前端服务器,也不会告警
配置读取
Value
在当前类是一个Bean的前提下,可以通过在成员变量(非static或者final)上面添加@Value注解,参数为${yaml中的坐标},若配置文件中没有这个坐标,则启动时会报错。
可以给个默认值提高容错性:1
冒号后可添加默认值或者不加(赋空值“”)
ConfigurationProperties
指定一个前缀,会将前缀下的所有配置注入到当前Bean的成员变量中Environment
容器中会有一个Spring暴露出来的Bean叫做Enviroment,可通过自动注入将其注入到当前环境,通过该Bean的getProperty(配置坐标)方法获取配置
或者可以通过实现EnvironmentAware接口去获取容器中的env对象PropertySource注解
可以指定其他的properties配置文件来进行读取,可通过一些配置读取自定义的yaml文件通过输入流的方式手动读取
使用getResourceAsStream获取jar包中输入流
SpringBoot默认AOP
spring默认行为是代理类有接口使用jdk代理,没有实现接口使用cglib,但springboot是强制所有都使用cglib来作为aop的实现,cglib进行代理时会动态生成字节码,这样可以获得接口实现类的信息比如方法注解,否则只能获取接口上的信息。其次使用CGlib可以使用接口或者实现类类型的变量来接受,但如果使用java原生AOP,则只能使用接口来接受,若该实现类没有接口,则会生成一个该类的子类对象为Bean
SpringBoot核心注解
- SpringBootApplication
- SpringBootConfiguration
- EnableAutoConfiguration
- ConditionalOn…
自动配置相关的注解,自动配置就是boot的特性,所以conditional也是
内置Tomcat
- 引入web依赖后,会引入服务器的自动配置,其中默认支持tomcat(通过conditionalOnClass:Tomcat.class),激活Tomcat的Factory配置
- SpringBoot启动时创建一个容器,同时加载Bean
- 此时会获取Tomcat的工厂Bean
- 通过工厂的getwebserver获取tomcat,启动并挂起
外部Tomcat
- 将项目打包方式设为war
- 从web依赖中将tomcat依赖排除
- 实现接口SpringBootServletInitializer并重写configure方法,在其中返回 builder.sources(启动类)
SPI
java中通过配置文件的方式,将一些实现类注册到配置文件中,在运行时使用ServiceLoader.load方法,获取配置文件中的对应类的对象?
读取配置文件原理
通过事件监听器的方式读取
默认日志实现框架
默认门面slf4j,默认实现logback
若要切换为log4j:排除logback,添加slf4j-log4j12调节器
若要切换为log4j2:排除掉logback,添加log4j2的starter
读取request请求体不完整
原本使用inputstream的available来获取报文大小,但使用inputStream.available()并不总是返回整个流的大小。它只返回可以无阻塞地从此输入流读取(或跳过)的字节数的估计值。在实际应用中,这可能导致只读取了部分数据。
获取不到完整的请求体内容是因为HTTP请求的正文(body)长度是动态的,而inputStream.available()方法返回的是在不阻塞的情况下可以从输入流中读取的字节数。当输入流中的数据量少于或等于输入流内部的缓冲区大小时,available()方法可能返回的是小于实际数据量的值,这就会导致最后只读取了部分数据。为了完整地读取HTTP请求的正文内容,需要使用一个循环来不断读取输入流直到没有更多数据可读。
1 | byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; |
注意这里的buffer大小会决定在转字符串时是否完整
启动后初始化
使用PostConstruct注解
在一个被spring代理的组件中使用该注解标记一个方法,方法名不固定,该方法会在当前bean中所有属性注入后调用
1 |
|
抽出公共模块,并引入公共模块中的配置
公共模块中配置文件命名可以参考:application-功能-环境.yaml,注意不要与其他模块中的配置文件同名
用到该公共模块的服务中,配置如下:
1 | spring: |
tomcat对文件上传大小的限制
1 | # 上传文件大小限制 |
接口参数校验
在实体类字段上进行校验规则的注解,在用到这些实体类的Controller上标记@Validated可以对所有Controller方法中,有进行字段校验的实体类进行校验,或者也可以直接标记在Controller方法,进行单个参数的校验。
1 | public class FeedbackInfo extends BaseEntity { |
1 |
|
@RequestParam
如果Params和Body的form中都有一个相同名字的key,则在通过@RequestParam获取该key的时候会将两个值同时获取并拼接
文件上传与下载
文件上传
1 | // contronller |
下载文件
1 | // controller |
Springboot升级3.2报错
问题一
Invalid value type for attribute ‘factoryBeanObjectType’: java.lang.String
原因,mybatis的实现中用到的api在springboot3.2后更改了
解决方法:使用mybtais plus 355
注意组件id与springboot2.几的时候不同,但不改居然也能下载东西
1 | <dependency> |
问题二
java.lang.IllegalStateException: No target Validator set
1 | <dependency> |
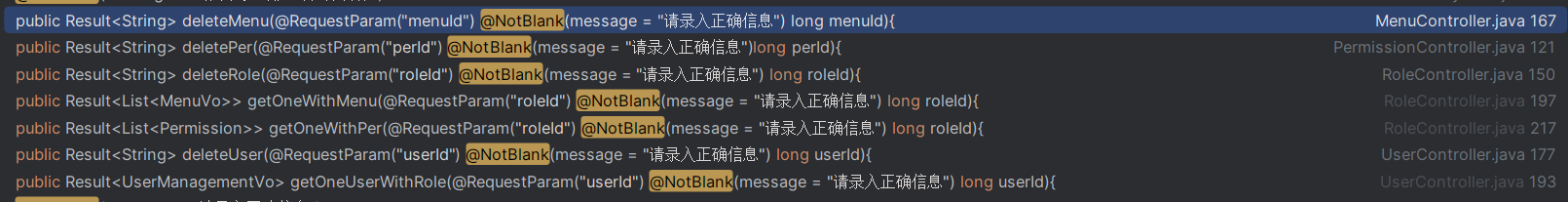
NotBlank不再支持数值类型,需要改为NotNull
LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime 反序列化问题
在实体类中使用LocalDateTime 类型接收字符串时,需要在字段上添加@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")注解,且pattern不可变,同时前端传值必须传时分秒
或者可自定义反序列化器.
1 | /** |
