nginx
基本概念
反向代理
对客户端隐藏服务器的真实位置,与正向代理(vpn)相反
负载均衡
轮询,加权轮询,iphash
动静分离
动态页面与静态页面交给不同的服务器解析
默认的配置文件
1 | #user nobody; |
整体的配置
1 | ... #全局块 |
配置含义
全局块
不会被{}包裹,全局块篇配置影响nginx全局的指令。一般有:运行nginx服务器的用户组、 nginx进程pid存放路径、日志存放路径、配置文件引入、允许生成worker process数等
events块
配置影响nginx服务器或与用户的网络连接。 比如:
- 每个进程的最大连接数
- 选取哪种事件驱动模型处理连接请求
- 是否允许同时接受多个网络连接
- 开启多个网络连接序列化
http块
可以嵌套多个server, 配置代理, 缓存, 日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置, 如文件引入, mime-type定义, 日志自定义, 是否使用sendfile传输文件, 连接超时时间,但链接请求数等.
server块
配置虚拟主机的相关参数, 一个http块中可以有多个server
location块
配置请求的路由, 以及各种页面的处理情况
1 | ... |
一个示例配置文件
1 | ########### 每个指令必须有分号结束。################# |
location规则
1 | location [= | ~ | ~* | ^~] uri { |
= : 用于不含正则表达式的uri前,要求请求字符串与uri严格匹配
代理转发
1 | server{ |
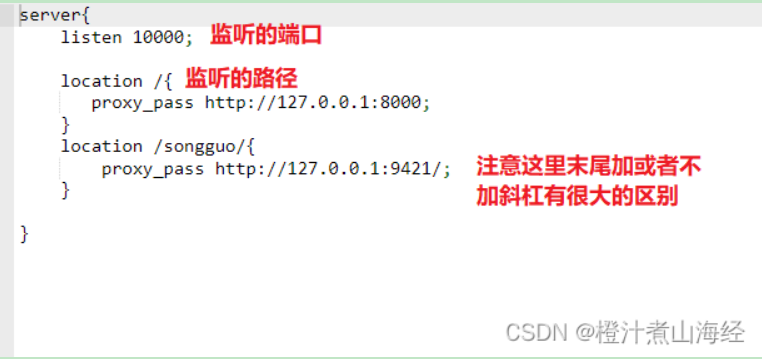
两种配置区别:
1 | upstream my_server{ |
前者会转发到 http://10.0.0.2:8080
后者会转发到 http://10.0.0.2:8080/my
也就是说,如果转发到的地址末尾不带/斜杠的话,转发时会带上过滤路径一起转发,而如果转发地址带/斜杠,则会去掉过滤地址转发。
负载均衡
1 | upstream mysvr { |
热备份
AAAAAAA挂了BBBBBBBB…………
1
2
3
4upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #热备
}轮询
ABABABABAB……………
1
2
3
4upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333;
}加权轮询
ABBABBABB………….
1
2
3
4upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878 weight=1;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 weight=2;
}iphash
1
2
3
4
5upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333;
ip_hash;
}
其他配置
- down,表示当前的server暂时不参与负载均衡。
- backup,预留的备份机器。当其他所有的非backup机器出现故障或者忙的时候,才会请求backup机器,因此这台机器的压力最轻。
- max_fails,允许请求失败的次数,默认为1。当超过最大次数时,返回proxy_next_upstream 模块定义的错误。
- fail_timeout,在经历了max_fails次失败后,暂停服务的时间。max_fails可以和fail_timeout一起使用。
1 | upstream mysvr { |
SNI导致的握手失败问题
原先配置
1 | location / { |
报错:
2023/12/11 05:49:02 [error] 23#23: *2 SSL_do_handshake() failed (SSL: error:0A000438:SSL routines::tlsv1 alert internal error:SSL alert number 80) while SSL handshaking to upstream, client: 172.17.0.1, server: localhost, request: “GET / HTTP/1.1”, upstream: “https://104.109.129.184:443/security/v1/oauth/token“, host: “localhost”
2023/12/11 05:49:02 [warn] 23#23: *2 upstream server temporarily disabled while SSL handshaking to upstream, client: 172.17.0.1, server: localhost, request: “GET / HTTP/1.1”, upstream: “https://104.109.129.184:443/security/v1/oauth/token“, host: “localhost”
开启SNI后解决
1 | location / { |
SNI:Server Name Indication是 TLS 的扩展,允许在握手过程开始时通过客户端告诉它正在连接的服务器的主机名称。作用:用来解决一个服务器拥有多个域名的情况。
后端已处理跨域后nginx再处理跨域出错
背景:后端设置了croswebfilter,nginx反向代理了后端,使得前端在访问后端时使用同源的域,同时也设置了跨域头的添加
情况:浏览器前端请求nginx代理的后端的时候报错,postman请求nginx代理的后端不报错
原因:后端通过header中是否有origin头来判断当前请求是否为跨域请求,如果当前请求为跨域请求,则会在响应头中添加允许跨域的头。而nginx的配置会在所有请求的响应头中添加跨域头,这样会造成冲突
解决:去掉后端的跨域处理
postman不报错的原因:postman没有同源限制,所以不会在请求中添加origin,故后端不会对该请求的响应头做处理
proxy_set_header和add_header的区别

proxy_set_header是nginx设置请求头给上游服务器,add_header是nginx设置响应头信息给浏览器。
假如nginx请求上游服务器时,添加额外的请求头,就需要使用proxy_set_header。在java中使用HttpServletRequest.getHeader(String name)来获取请求头的值,name是请求头的名称。
1 | 语法格式: |
nginx响应数据时,要告诉浏览器一些头信息,就要使用add_header。例如跨域访问
1 | add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '*'; |
nginx代理后端
conf.d下文件:
1 | error_log /etc/nginx/log/error_log debug; |
try_files
参数$uri为当前请求的路径,try_files后跟的参数为从前向后匹配,若都匹配不到则直接请求最后一个参数,最后一个参数可以是真实存在的文件,也可以是等号+状态码,比如=404
1 | try_files $uri $uri.html $uri/ =404; |
缓冲区大小
get 请求下载文件时,net::ERR_INCOMPLETE_CHUNKED_ENCODING 200 (OK)
nginx配置缓冲区设置过小;nginx的临时目录(/proxy_temp)没有权限写入缓存文件;
超时时间
nginx:如何在Nginx中设置超时时间?请列举各种超时配置_nginx超时时间设置-CSDN博客
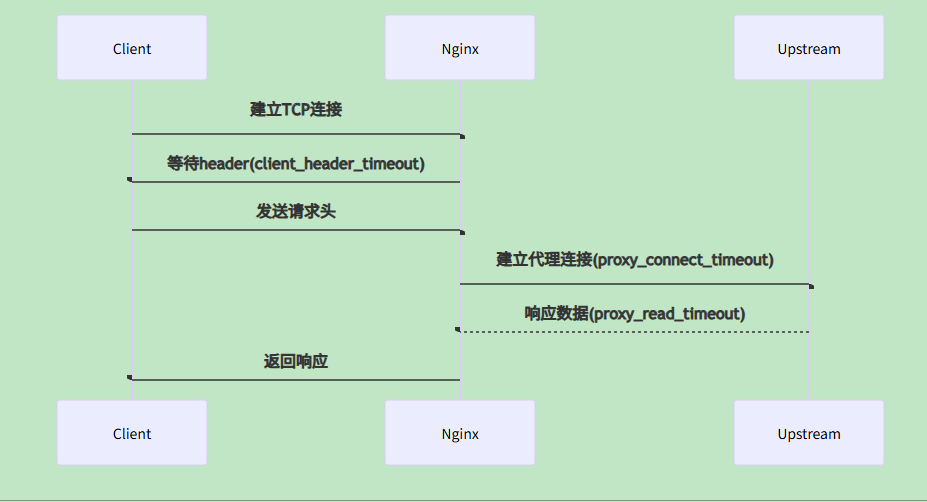
| 客户端连接超时 | client_header_timeout |
60s | 防止慢速HTTP攻击 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 客户端请求体读取超时 | client_body_timeout |
60s | 大文件上传场景 |
| 代理连接超时 | proxy_connect_timeout |
60s | 上游服务网络不稳定时 |
| 代理读取超时 | proxy_read_timeout |
60s | 长轮询/SSE连接 |
| 代理发送超时 | proxy_send_timeout |
60s | 低速客户端场景 |
| Keepalive连接超时 | keepalive_timeout |
75s | 高并发短连接优化 |
| DNS解析超时 | resolver_timeout |
30s | 动态上游服务发现 |
